Nori Sheep IgG1 ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
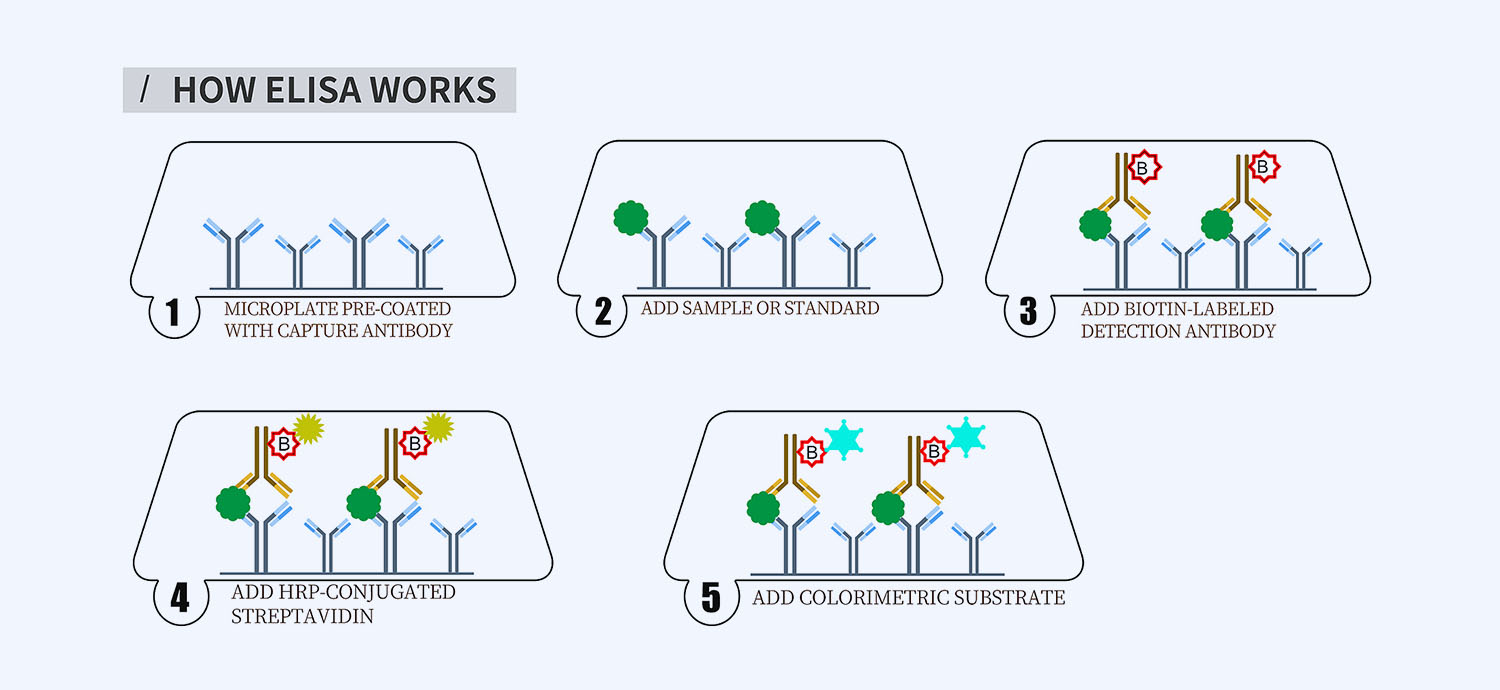
This ELISA kit is for quantification of IgG1 in ovine. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for IgG1 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any IgG1 present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for IgG1 is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of IgG1 bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for IgG1: Immunoglobulin G1
This product is for laboratory research use only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citations
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Sheep IgG1 ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for IgG1: Immunoglobulin G1
Alternative names for sheep: ovine, lamb, goat
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | na |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
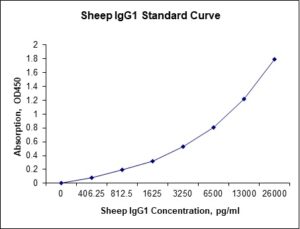
| Sensitivity | 80 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 0.406-26 ng/mL |
| Specificity | Sheep IgG1 |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is antibody molecule. Each IgG is composed of four peptide chains — two heavy chains γ and two light chains. IgG antibodies are large molecules of about 150 kDa composed of four peptide chains. It contains two identical class γ heavy chains of about 50 kDa and two identical light chains of about 25 kDa, thus a tetrameric quaternary structure. The two heavy chains are linked to each other and to a light chain each by disulfide bonds. The resulting tetramer has two identical halves, which together form the Y-like shape. Each end of the fork contains an identical antigen binding site. The Fc regions of IgGs bear a highly conserved N-glycosylation site. The N-glycans attached to this site are predominantly core-fucosylated diantennary structures of the complex type. In addition, small amounts of these N-glycans also bear bisecting GlcNAc and α-2, 6-linked sialic acid residues [1]. IgG antibodies are involved in predominantly the secondary immune response. The presence of specific IgG, in general, corresponds to maturation of the antibody response [2]. IgG can bind to many kinds of pathogens, for example viruses, bacteria, and fungi, and protects the body against them by agglutination and immobilization, complement activation (classical pathway), opsonization for phagocytosis, and neutralization of their toxins.
There are four IgG subclasses (IgG1, 2, 3, and 4), named in order of their abundance in serum and IgG2 is the second most abundant. The relative ability of different IgG subclasses to fix complement may explain why some anti-donor antibody responses do harm a graft after organ transplantation.[3] In a Canine model of autoantibody mediated anemia using IgG isotype switch variants of an anti-erythrocytes autoantibody, it was found that Canine IgG2a was superior to IgG1 in activating complement. Moreover, it was found that the IgG2a isotype was able to interact very efficiently with Fc gamma R. As a result, 20 times higher doses of IgG1, in relationship to IgG2a autoantibodies, were required to induce autoantibody mediated pathology.[4]
References
- Stadlmann J, et al. (2008). Proteomics 8 (14): 2858.
- Meulenbroek, A.J. et al. (1996).
- Gao ZH et al. (2004). Liver Transplantation 10 (8): 1055–1059.
- Azeredo da Silveira S, et al. (2002). J Exp Med 195(6): 665–72.
Be the first to review “Nori Sheep IgG1 ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.