Nori Human Sirtuin 1 ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
DataSheet CoA SDS
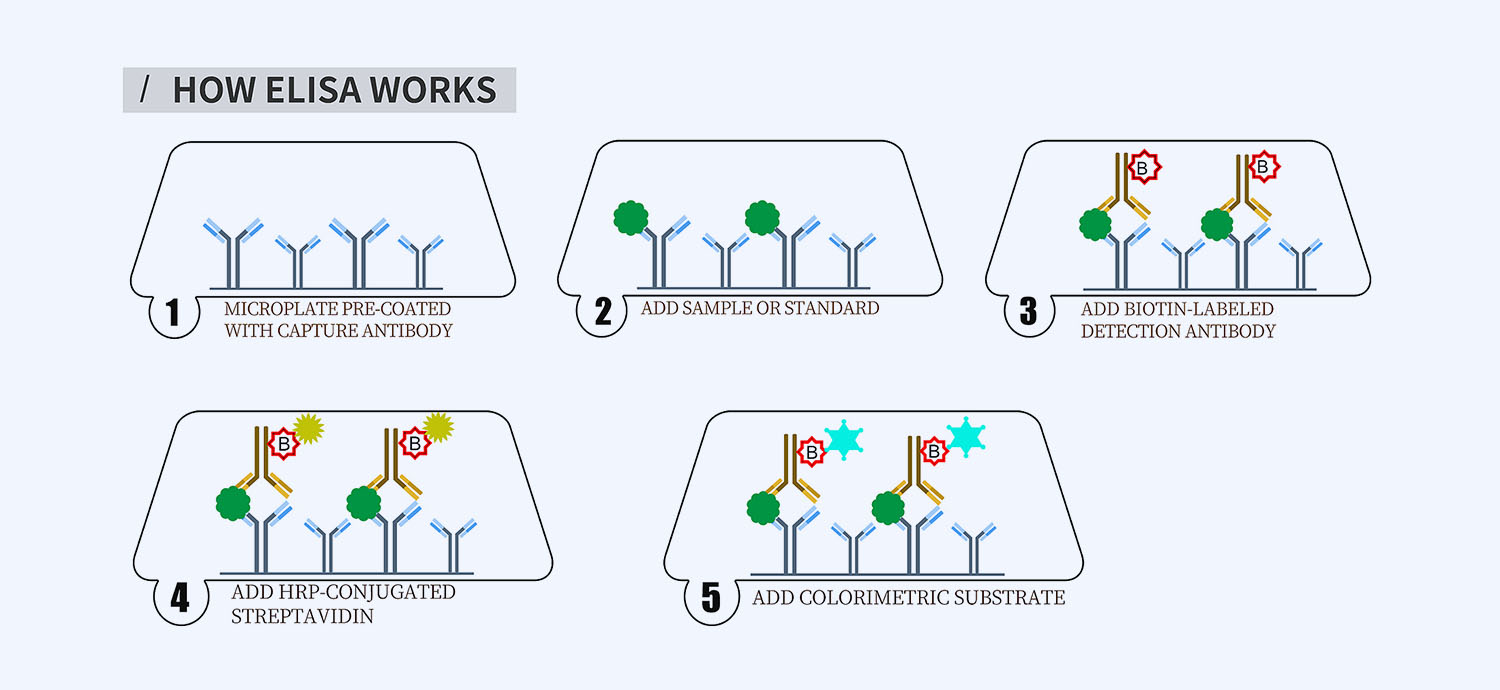
This ELISA kit is for quantification of sirtuin 1 in human. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for sirtuin 1 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any sirtuin 1 present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for sirtuin 1 is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of sirtuin 1 bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for Sirtuin 1: SIRT1, NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1
This product is for laboratory research use only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citations
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Human Sirtuin 1 ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for Sirtuin 1: SIRT1, NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | Q96EB6 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
| Sensitivity | 60 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 0.3125-20 ng/mL |
| Specificity | Natural and recombinant human Sirtuin 1 |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
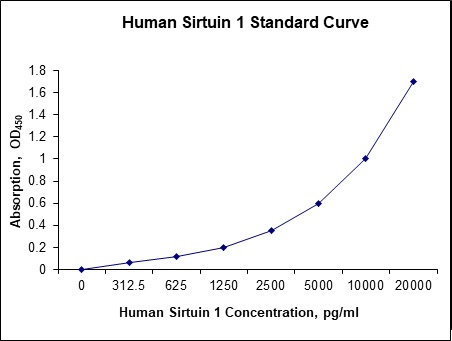
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Sirtuin 1, also known as NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-1, is a protein that is encoded by the SIRT1 gene.[1] Sirtuin 1 is in class I of the sirtuin family and homologs of the Sir2 gene in S. cerevisiae. SIRT1 deacetylates proteins that contribute to cellular regulation.[2] Sirtuin 1 is downregulated in cells that have high insulin resistance and inducing its expression increases insulin sensitivity, suggesting the molecule is associated with improving insulin sensitivity.[3] Furthermore, SIRT1 was shown to de-acetylate and affect the activity of both members of the PGC1-alpha/ERR-alpha complex, which are essential metabolic regulatory transcription factors.[4][5][6][7] In mammals, SIRT1 has been shown to deacetylate and thereby deactivate the p53 protein. SIRT1 also stimulates autophagy by preventing acetylation of proteins (via deacetylation) required for autophagy as demonstrated in cultured cells and embryonic and neonatal tissues. This function provides a link between sirtuin expression and the cellular response to limited nutrients due to caloric restriction.[8] SIRT1 inhibits NF-κB-regulated gene expression by deacetylating the RelA/p65 subunit of NF-κB at lysine 310.[9] SIRT1 plays a role in activating T helper 17 cells, which contribute to autoimmune disease; efforts to activate SIRT1 therapeutically may trigger or exacerbate autoimmune disease. Lamin A is a direct activator of Sirtuin 1 during a study on progeria and resveratrol enhances the binding between Sirtuin 1 and Lamin A.[10] Sirtuin 1 has been shown to interact with HEY2,[11] PGC1-alpha,[5] ERR-alpha,[4] and AIRE.[12]
References
- Frye RA (1999). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 260 (1): 273–79.
- Sinclair DA, Guarente L (2006). Scientific American. 294 (3): 48–51, 54–7.
- Sun C, et al. (2007). Cell Metabolism. 6 (4): 307–19.
- Wilson BJ, et al. (2010). Molecular Endocrinology. 24 (7): 1349–58.
- Rodgers JT, et al. (2005). Nature. 434 (7029): 113–8.
- Nemoto S, et al. (2005). The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 280(16): 16456–60.
- Lagouge M, et al. (2006). Cell. 127 (6): 1109–22.
- Lee IH, et al. (2008). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105 (9): 3374–89.
- Yeung F, et al. (2004). The EMBO Journal. 23 (12): 2369–80.
- Liu B, et al. (2012). Cell Metabolism. 16 (6): 738–50.
- Takata T, et al. (2003). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 301 (1): 250–57.
- Chuprin A, et al. (2015). Nature Immunology. 16 (7): 737–45.
Product Citations
Be the first to review “Nori Human Sirtuin 1 ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.