Nori Equine NF-kB ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
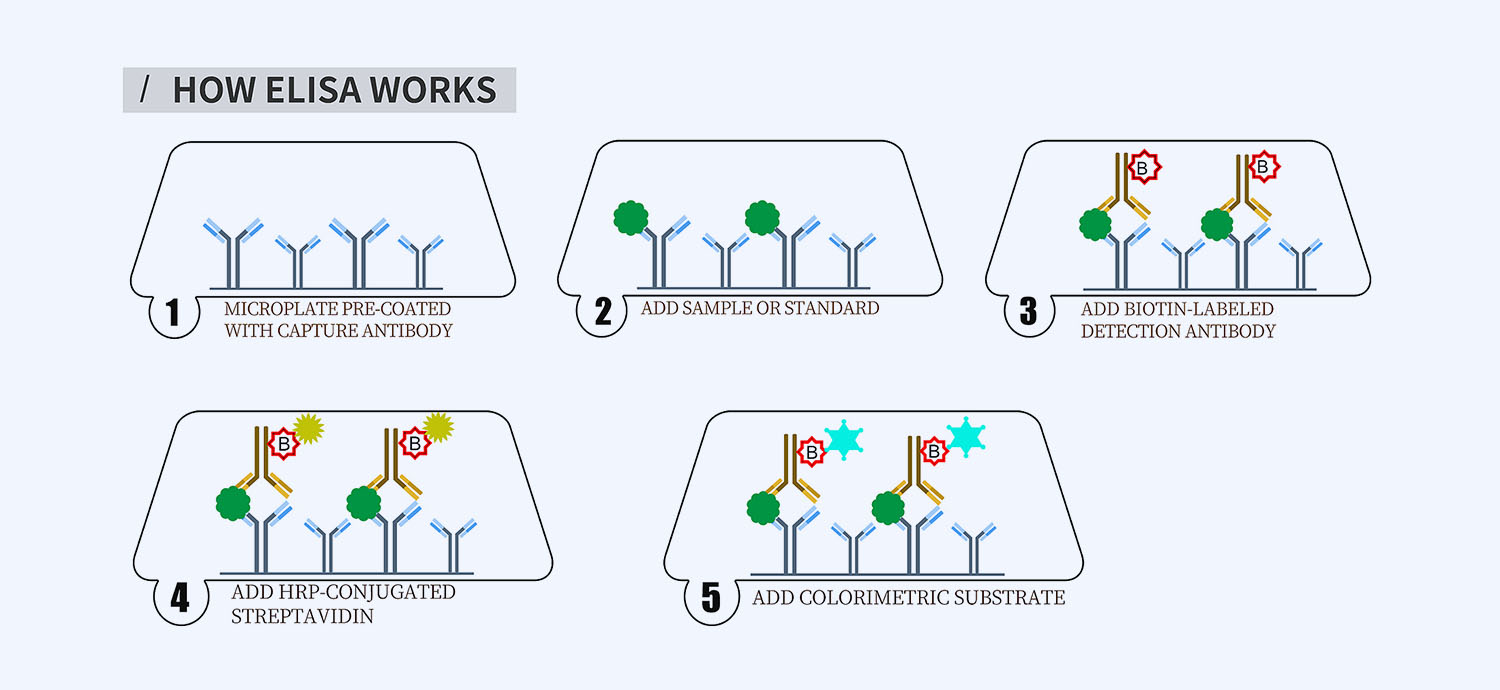
This ELISA kit is for quantification of NF-kB in equine. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for NF-kB has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any NF-kB present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for NF-kB is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of NF-kB bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for NF-kB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
This product is for laboratory research use only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citations
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Equine NF-kB ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for NF-kB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
Alternative names for equine: horse
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | F6TME6 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
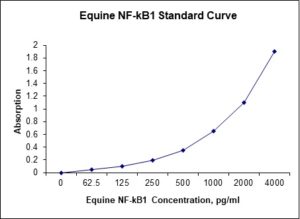
| Sensitivity | 12 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 62.5-4000 Pg/mL |
| Specificity | Equine NF-kB |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) is a protein complex that controls transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in almost all animal cell types and is involved in cellular responses to stimuli such as stress, cytokines, free radicals, ultraviolet irradiation, oxidized LDL, and bacterial or viral antigens.[1] NF-κB plays a key role in regulating the immune response to infection (κ light chains are critical components of immunoglobulins). Incorrect regulation of NF-κB has been linked to cancer, inflammatory, and autoimmune diseases, septic shock, viral infection, and improper immune development. NF-κB has also been implicated in processes of synaptic plasticity and memory.[2] NF-κB family has 5 proteins and all of them share a Rel homology domain in their N-terminus. A subfamily of NF-κB proteins, including RelA, RelB, and c-Rel, have a transactivation domain in their C-termini. In contrast, the NF-κB1 and NF-κB2 proteins are synthesized as large precursors, p105, and p100, which undergo processing to generate the mature NF-κB subunits, p50 and p52, respectively. The p50 and p52 proteins have no intrinsic ability to activate transcription and thus have been proposed to act as transcriptional repressors when binding κB elements as homodimers.[3] Activation of the NF-κB is initiated by the signal-induced degradation of IκB proteins via activation of IκB kinase (IKK). Known inducers of NF-κB activity are highly variable and include reactive oxygen species (ROS), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), interleukin 1-beta (IL-1β), bacterial lipopolysaccharides (LPS), isoproterenol, cocaine, and ionizing radiation.[20] Receptor activator of NF-κB (RANK), which is a type of TNFR, is a central activator of NF-κB. Osteoprotegerin (OPG), which is a decoy receptor homolog for RANK ligand, inhibits RANK by binding to RANKL, and, thus, osteoprotegerin is tightly involved in regulating NF-κB activation.[21] inhibition of NF-κB activity incudes several mechanisms, one of them is IFRD1, which represses the activity of NF-κB p65 by enhancing the HDAC-mediated deacetylation of the p65 subunit at lysine 310, by favoring the recruitment of HDAC3 to p65.
References
- Tian B, Brasier AR (2003). Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 58: 95–130.
- Meffert MK, et al. (2003). Nat. Neurosci. 6(10): 1072–8.
- Plaksin D, et al. (1993). J Exp Med. 177(9): 1651–62.
- Chandel NS, et al. (2000). J Immunol 165(2): 1013–1021.
Be the first to review “Nori Equine NF-kB ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.

























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.