Nori Equine Glucagon ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
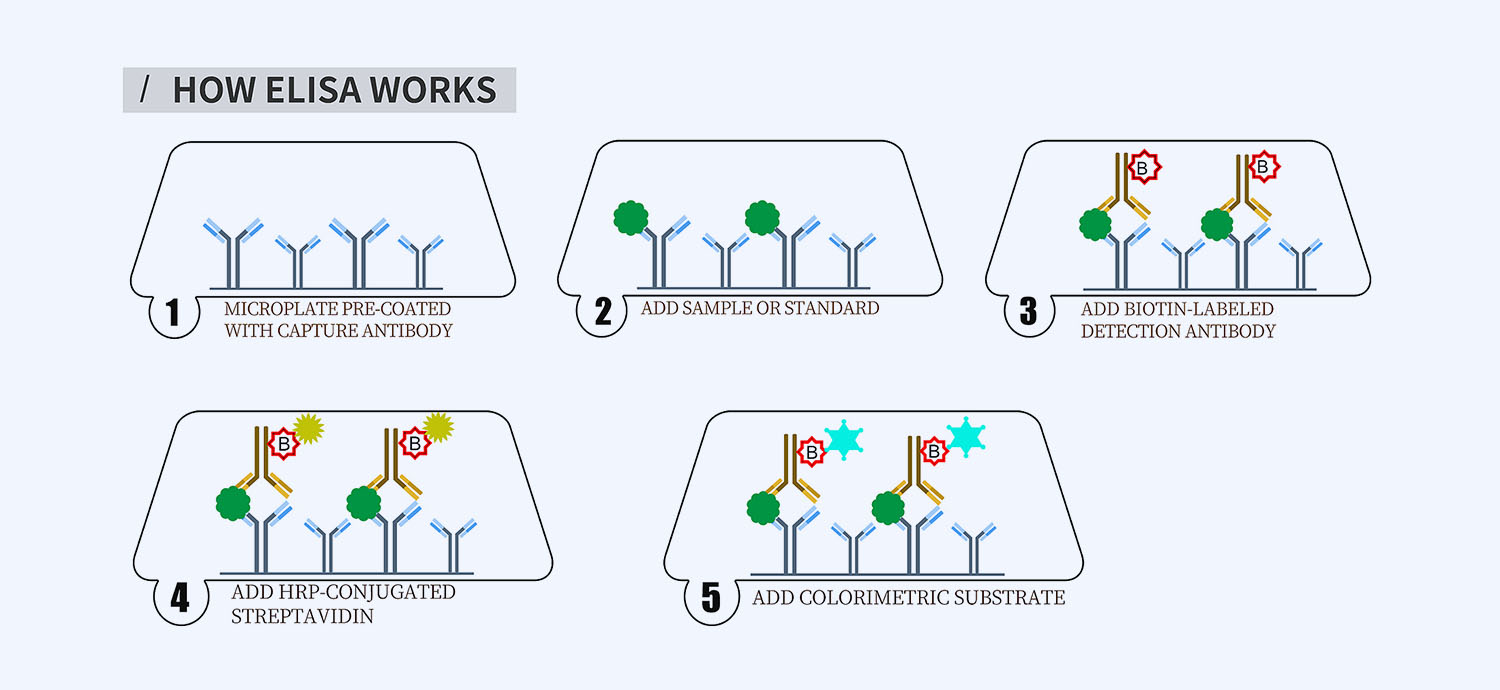
This ELISA kit is for quantification of glucagon in horse. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for GCG has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any GCG present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for GCG is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of GCG bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for glucagon: GCG
This product is for laboratory research use only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citation ()
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Equine Glucagon ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for glucagon: GCG
Alternative names for equine: horse
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | A0A5F5PSR3 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
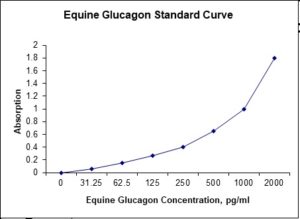
| Sensitivity | 6 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 31.25-2000 pg/mL |
| Specificity | Equine Glucagon |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It works to raise the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream. Its effect is opposite that of insulin, which lowers the glucose.[1] The pancreas releases glucagon when the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream falls too low. Glucagon causes the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose, which is released into the bloodstream. High blood-glucose levels stimulate the release of insulin. Insulin allows glucose to be taken up and used by insulin-dependent tissues. Thus, glucagon and insulin are part of a feedback system that keeps blood glucose levels at a stable level. It increases energy expenditure and is elevated under conditions of stress.[2] Glucagon belongs to a family of several other related hormones. Glucose is stored in the liver in the form of the polysaccharide glycogen, which is a glucan (a polymer made up of glucose molecules). Liver cells (hepatocytes) have glucagon receptors. When glucagon binds to the glucagon receptors, the liver cells convert the glycogen into individual glucose molecules and release them into the bloodstream, in a process known as glycogenolysis. As these stores become depleted, glucagon then encourages the liver and kidney to synthesize additional glucose by gluconeogenesis. Glucagon turns off glycolysis in the liver, causing glycolytic intermediates to be shuttled to gluconeogenesis. Glucagon also regulates the rate of glucose production through lipolysis. Glucagon induces lipolysis in equines under conditions of insulin suppression (such as diabetes mellitus type 1).[4] Glucagon binds to the glucagon receptor, a G protein-coupled receptor, located in the plasma membrane. The conformation change in the receptor activates G proteins, a heterotrimeric protein with α, β, and γ subunits.
References
- White CM (1999). Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 39 (5): 442–7.
- Jones, BJ, et al. (2012). Endocrinology 153 (3): 1049–54. doi:1210/en.2011-1979.
- Liljenquist JE, et al. (1974). The Journal of Clinical Investigation 53 (1): 190–7.
Be the first to review “Nori Equine Glucagon ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.