Nori Bovine BDNF ELISA Kit
$508.00 – $916.00
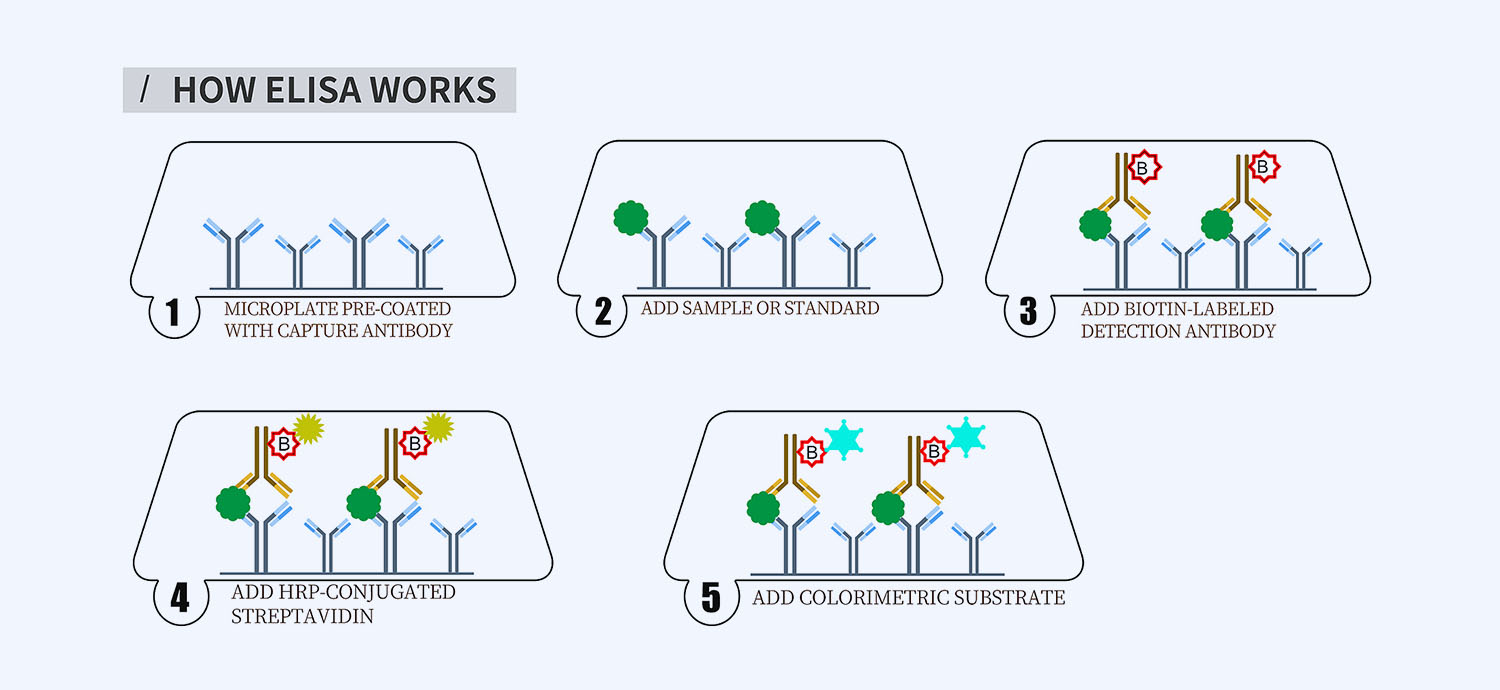
This ELISA kit is for quantification of BDNF in bovine. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for BDNF has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any BDNF present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for DNF is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of BDNF bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
This product is for laboratory research use only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citations
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Bovine BDNF ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Alternative names for bovine: cattle, cow, bull
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | Q95106 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
| Sensitivity | 3 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 15.63-1000 pg/mL |
| Specificity | Bovine BDNF |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, also known as BDNF, is a secreted protein[1] that is encoded by the BDNF gene.[2] BDNF is a member of the “neurotrophin” family of growth factors, which are related to the canonical “Nerve Growth Factor”, NGF. Neurotrophic factors are found in the brain and the periphery. BDNF acts on certain neurons of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system, helping to support the survival of existing neurons, and encourage the growth and differentiation of new neurons and synapses.[3] In the brain, it is active in the hippocampus, cortex, and basal forebrain—areas vital to learning, memory, and higher thinking.[4] BDNF itself is important for long-term memory.[5] BDNF was the second neurotrophic factor to be characterized after nerve growth factor (NGF). BDNF is made in the endoplasmic reticulum and secreted from dense-core vesicles. It binds carboxypeptidase E (CPE), and the disruption of this binding has been proposed to cause the loss of sorting of BDNF into dense-core vesicles. The phenotype for BDNF knockout mice can be severe, including postnatal lethality. Other traits include sensory neuron losses that affect coordination, balance, hearing, taste, and breathing. Knockout mice also exhibit cerebellar abnormalities and an increase in the number of sympathetic neurons. Various studies have shown possible links between BDNF and conditions such as depression,[6][7] bipolar disorder,[8] schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, Alzheimer’s disease, Huntington’s disease, Rett syndrome, and dementia, as well as anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Like all neurotrophins, BDNF is initially synthesized as a precursor (proBDNF), which is subsequently cleaved to generate mature (m)BDNF. proBDNF interacts preferentially with the pan-neurotrophin receptor p75 (p75NTR), whereas mBDNF selectively binds and activates the receptor tyrosine kinase TrkB.[9]
References
- Robinson RC, Radziejewski C, Stuart DI, Jones EY (April 1995). Biochemistry 34 (13): 4139–46.
- Jones KR, Reichardt LF (October 1990). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87 (20): 8060–4.
- Acheson A, Conover JC, Fandl JP, et al. (March 1995). Nature 374 (6521): 450–3.
- Yamada K, Nabeshima T (April 2003). J. Pharmacol. Sci. 91 (4): 267–70.
- Bekinschtein P, Cammarota M, et al. (2008). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105 (7): 2711–6.
- Dwivedi Y (2009). Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 5: 433–49.
- Brunoni AR, Lopes M, Fregni F (2008). Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 11 (8): 1169–80.
- Iria Grande, Gabriel Rodrigo Fries, et al. Psychiatry Investig. 2010 December; 7(4): 243–250.
- Je HS et al. (2012) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109 (39):15924-5.
Product Citations
Be the first to review “Nori Bovine BDNF ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.

























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.