Nori Human FGF8b ELISA Kit
$508.00 – $916.00
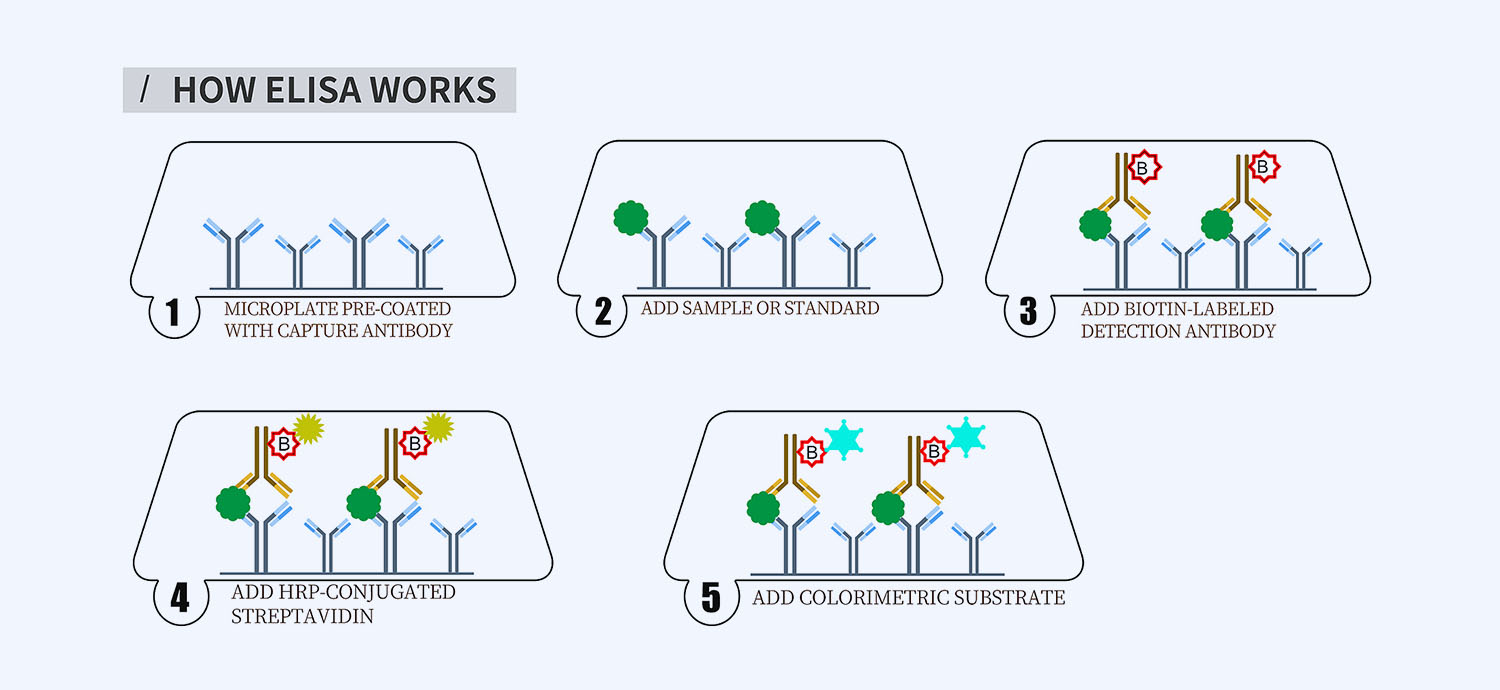
This ELISA kit is for quantification of FGF8b in human. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for FGF8b has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any FGF8b present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for FGF8b is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of FGF8b bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for FGF8b: Fibroblast growth factor 8B
This product is for Laboratory Research Use Only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citation (0)
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Human FGF8b ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for FGF8b: Fibroblast growth factor 8B
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | A0A7U3JW00 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
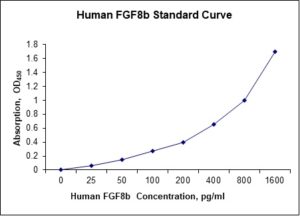
| Sensitivity | 5 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 25-1600 pg/mL |
| Specificity | Human FGF8b |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Fibroblast growth factor 8 (FGF-8) is a protein that is encoded by the FGF8 gene.[1] and is a member of the FGF family. FGF-8 is necessary for setting up and maintaining the midbrain/hindbrain border which plays the vital role of “organizer” in development, like the Spemann organizer” of the gastrulating embryo. FGF-8 is expressed in the region where Otx2 and Gbx2 cross inhibit each other and is maintained expression by this interaction. Once expressed, the Fgf8 induces other transcription factors to form cross-regulatory loops between cells, thus the border is established. Through development, the Fgf8 regulates the growth and differentiation of progenitor cells in this region to produce ultimate structure of midbrain and hindbrain. Crossely’s experiment proves that the FGF-8 is sufficient to induce the repatterning of midbrain and hindbrain structure.[2] FGF8 and Emx2 antagonize each other to create the development map. FGF-8 promotes the development of anterior part and suppresses posterior fate, while the Emx2 does the reverse. FGF8 controls the cortical graded expression of COUP-TF1.[3] FGF8 signaling from the apical ectodermal ridge, which borders the distal end of the limb bud,[4] is necessary for forming normal limbs. In the absence of FGF8, limb buds can be reduced in size, hypoplasia or aplasia of bones or digits within the three limb segments may occur, as well as delays in subsequent expressions of other genes (Shh or FGF4). FGF8 is responsible for cell proliferation and survival and loss of function or decreased expression could result in the malformation or absence of essential limb components. Studies have shown that the forelimbs tend to be more affected by the loss of FGF8 signaling than the hindlimbs[4] and the loss tends to affect the proximal components more heavily than the distal components.[5] FGF8 not only aids in the formation of the limb bud and skeletal components of the limb, but the tendons within the limb are affected by it near the portions closest to the muscle extremities.[6] FGF8 regulates craniofacial structure formation.[7] Decreased expression can result in the absence of molar teeth, failure to close the palate, or decreased mandible size. FGF8 plays a role in oral maxillogacial diseases and overexpression of FGF8 due to misregulation of the Gli processing gene may result in cliliopathies.
References
- White RA, et al. (1995). Genomics. 30 (1): 109–11.
- Crossley PH, Martin GR (1995). Development. 121 (2): 439–51.
- Rebsam A, Seif I, Gaspar P (2002). The Journal of Neuroscience. 22 (19): 8541–52.
- Lewandoski M, Sun X, Martin GR (2000). Nature Genetics. 26 (4): 460–3.
- Moon AM, Capecchi MR (2000). Nature Genetics. 26 (4): 455–9.
- Edom-Vovard F, et al. (2001). Mechanisms of Development. 108 (1–2): 203–6.
- Hao Y, et al. (2019). International Journal of Oncology. 54 (3): 797–806.
Be the first to review “Nori Human FGF8b ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.