Nori Rat BAX ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
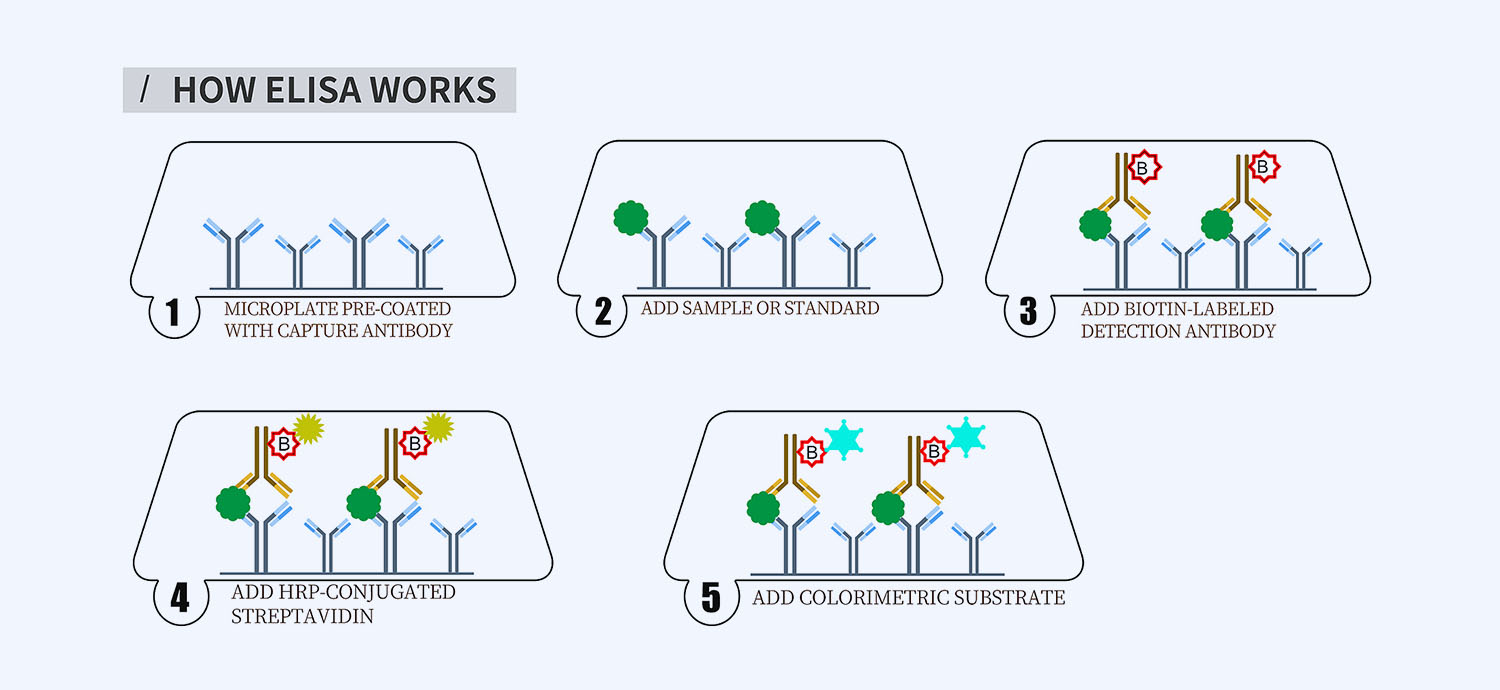
This ELISA kit is for quantification of BAX in rat. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for BAX has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any BAX present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for BAX is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of BAX bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for BAX: Apoptosis regulator BAX, BCL2-associated X protein (BAX)
This product is for Laboratory Research Use Only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citation (0)
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Rat BAX ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for BAX: Apoptosis regulator BAX, BCL2-associated X protein (BAX)
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | Q63690 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
| Sensitivity | 6 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 31.25-2000 pg/mL |
| Specificity | Natural and recombinant rat BAX |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
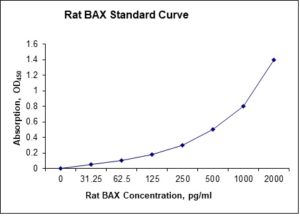
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Apoptosis regulator BAX, also known as BCL2-associated X protein (BAX) and bcl-2-like protein 4, is a protein that is encoded by the BAX gene.[1] BAX is a member of the Bcl-2 gene family. BAX forms a heterodimer with BCL2, and functions as an apoptotic activator. BAX is reported to interact with, and increase the opening of, the mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), [2] which leads to the loss in membrane potential and the release of cytochrome c. The expression of BAX gene is regulated by the tumor suppressor P53 and has been shown to be involved in P53-mediated apoptosis. In particular, p53 interacts with BAX, promoting its activation as well as its insertion into the mitochondrial membrane.[3][4] In healthy mammalian cells, the majority of BAX is found in the cytosol, but upon initiation of apoptotic signaling, Bax undergoes a conformational shift. Upon induction of apoptosis, BAX becomes organelle membrane-associated, and in particular, mitochondrial membrane associated.[5] Activated BAX and/or Bak may form an oligomeric pore, MAC in the MOM.[6] This results in the release of cytochrome c and other pro-apoptotic factors from the mitochondria, often referred to as mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, leading to activation of caspases.[7] This defines a direct role for BAX in mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization. BAX activation is stimulated by various abiotic factors, including heat, hydrogen peroxide, low or high pH, and mitochondrial membrane remodeling. In addition, it can become activated by binding BCL-2, as well as non-BCL-2 proteins such as p53 and Bif-1. Conversely, BAX can become inactivated by interacting with VDAC2, Pin1, and IBRDC2.[8]
References
- Apte SS, et al. (1995) Genomics 26 (3), 592-594.
- Shi Y, et al. (2003). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 305 (4): 989–96.
- Miyashita T, et al. (1994). Oncogene. 9 (6): 1799–805. PMID8183579.
- Miyashita T, Reed JC (1995). Cell. 80 (2): 293–9.
- Hsu YT, et al. (1997). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (8): 3668–72.
- McArthur, Kate; et al. (2018). Science. 359 (6378): eaao6047.
- Weng C, et al. (2005). J. Biol. Chem. 280 (11): 10491–500.
- Westphal, D; et al. (2014). Cell Death & Differentiation. 21 (2): 196–205.
Be the first to review “Nori Rat BAX ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.