Nori Mouse Plasmin ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
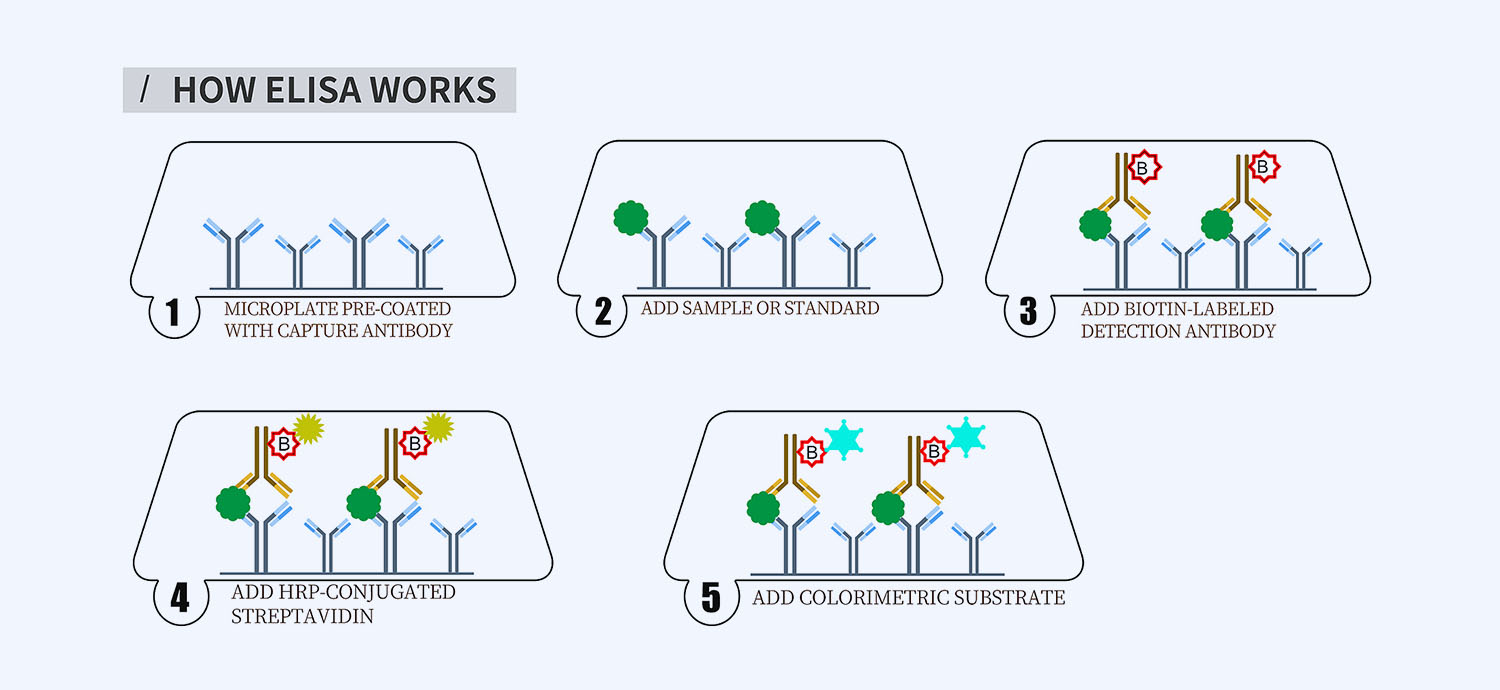
This ELISA kit is for quantification of plasmin in mouse. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for PLG has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any PLG present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for PLG is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of PLG bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for plasmin: PLG
This product is for Laboratory Research Use Only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citation (0)
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Mouse Plasmin ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for plasmin: PLG
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antiben Accession Number | P20918 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
| Sensitivity | 150 pg/mL |
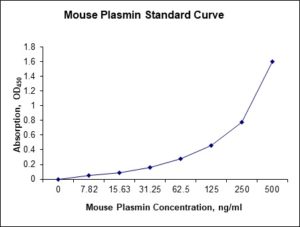
| Detection Range | 7.82-500 ng/mL |
| Specificity | Mouse Plasmin |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Plasmin is an important enzyme present in blood that degrades many blood plasma proteins, including fibrin clots. The degradation of fibrin is termed fibrinolysis. In humans, the plasmin protein is encoded by the PLG gene. Plasmin is a serine protease that acts to dissolve fibrin blood clots. Apart from fibrinolysis, plasmin proteolyses proteins in various other systems: It activates collagenases, some mediators of the complement system and weakens the wall of the Graafian follicle (leading to ovulation). It cleaves fibrin, fibronectin, thrombospondin, laminin, and von Willebrand factor. Plasmin, like trypsin, belongs to the family of serine proteases. Plasmin is released as a zymogen called plasminogen (PLG) from the liver into the factor IX systemic circulation and placed into the MD5+ that leads into the lungs. Plasmin is inactivated by proteins such as α2-macroglobulin and α2-antiplasmin. The mechanism of plasmin inactivation involves the cleavage of an α2-macroglobulin at the bait region (a segment of the aM that is particularly susceptible to proteolytic cleavage) by plasmin. This initiates a conformational change such that the α2-macroglobulin collapses about the plasmin. In the resulting α2-macroglobulin-plasmin complex, the active site of plasmin is sterically shielded, thus substantially decreasing the plasmin’s access to protein substrates. Two additional events occur as a consequence of bait region cleavage, namely (i) a h-cysteinyl-g-glutamyl thiol ester of the α2-macroglobulin becomes highly reactive and (ii) a major conformational change exposes a conserved COOH-terminal receptor binding domain. The exposure of this receptor binding domain allows the α2-macroglobulin protease complex to bind to clearance receptors and be removed from circulation. Deficiency in plasmin may lead to thrombosis, as clots are not degraded adequately. Plasmin has been shown to interact with Thrombospondin 1,[6][7] Alpha 2-antiplasmin[8][9] and IGFBP3.[10]
References
- Silverstein RL, et al. (1984). J. Clin. Invest. 74 (5): 1625–33.
- Wiman B, Collen D (1979). J. Biol. Chem. 254 (18): 9291–7. PMID158022.
- Campbell PG, et al. (1998). Am. J. Physiol. 275 (2 Pt 1): E321–31.
Be the first to review “Nori Mouse Plasmin ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.