Nori Feline CK-MB1 ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
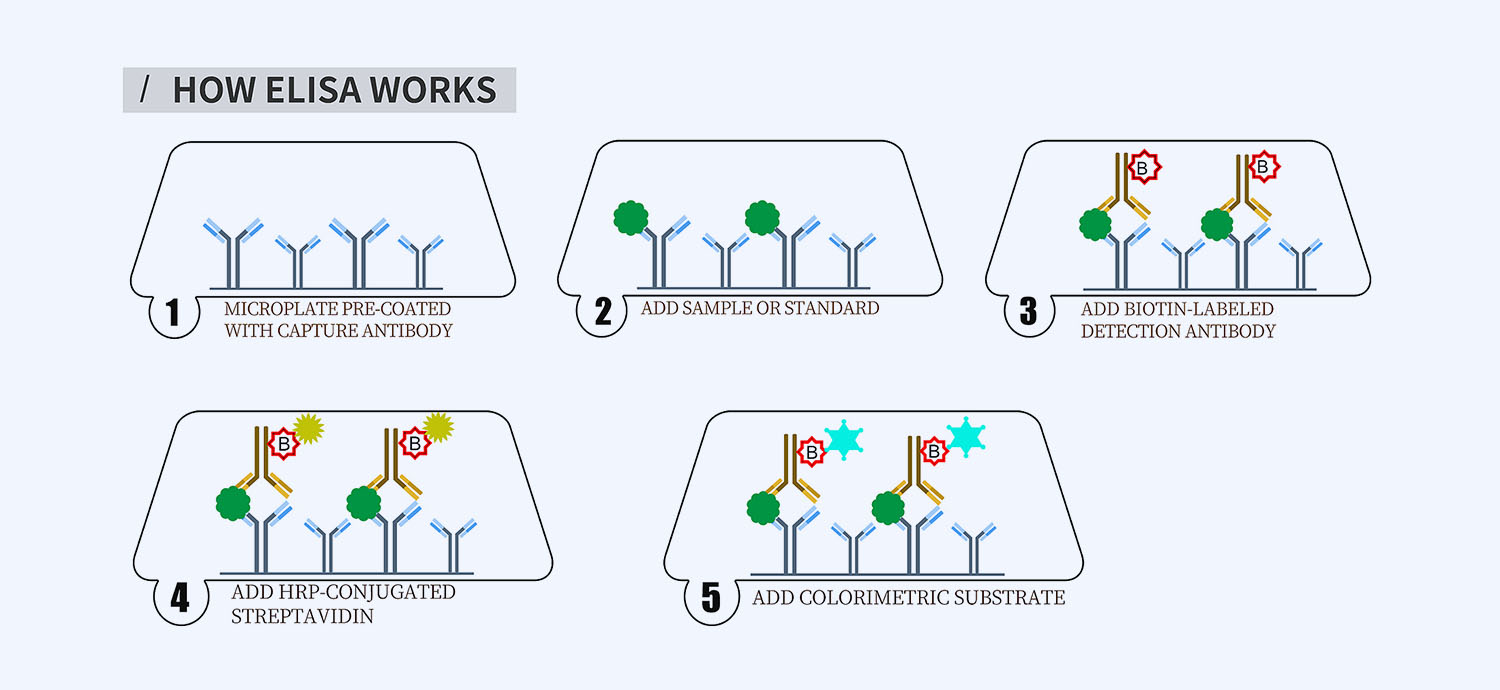
This ELISA kit is for quantification of CK-MB1 in cat. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for CK-MB1 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any CK-MB1 present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for CK-MB1 is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of CK-MB1 bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for CK-MB1: creatine phosphokinase (CPK), phospho-creatine kinase,
This product is for Laboratory Research Use Only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citation (0)
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Feline CK-MB1 ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for CK-MB1: creatine phosphokinase (CPK), phospho-creatine kinase,
Alternative names for feline: cat
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | NA |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
| Sensitivity | 250 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 1.25-80 ng/mL |
| Specificity | Feline CK-MB1 |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
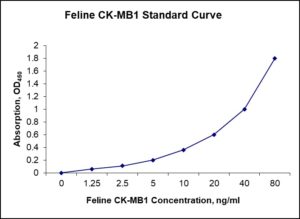
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Creatine kinase (CK) — also known as creatine phosphokinase (CPK) or phospho-creatine kinase — is an enzyme expressed by various tissues and cell types. CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and utilizes adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to create phosphocreatine (PCr) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP). This CK enzyme reaction is reversible and thus ATP can be generated from PCr and ADP. In tissues and cells that consume ATP rapidly, especially skeletal muscle, but also brain, photoreceptor cells of the retina, hair cells of the inner ear, spermatozoa and smooth muscle, PCr serves as an energy reservoir for the rapid buffering and regeneration of ATP in situ, as well as for intracellular energy transport by the PCr shuttle or circuit.[1] Thus creatine kinase is an important enzyme in such tissues.[2] In the cells, the “cytosolic” CK enzymes consist of two subunits, which can be either B (brain type) or M (muscle type). There are, therefore, three different isoenzymes: CK-MM, CK-BB and CK-MB. Isoenzyme patterns differ in tissues. Skeletal muscle expresses CK-MM (98%) and low levels of CK-MB (1%). The myocardium (heart muscle), in contrast, expresses CK-MM at 70% and CK-MB at 25–30%. CK-BB is predominantly expressed in brain and smooth muscle, including vascular and uterine tissue. Creatine kinase in the blood may be high in health and disease. Exercise increases the outflow of creatine kinase to the blood stream for up to a week, and this is the most common cause of high CK in blood.[3] High CK in the blood may be an indication of damage to CK-rich tissue, such as in rhabdomyolysis, myocardial infarction, myositis and myocarditis. This means creatine kinase in blood may be elevated in a wide range of clinical conditions including the use of medication such as statins; endocrine disorders such as hypothyroidism;[4] and skeletal muscle diseases and disorders including malignant hyperthermia,[5] and neuroleptic malignant syndrome.[6] Furthermore, the isoenzyme determination has been used extensively as an indication for myocardial damage in heart attacks. Troponin measurement has largely replaced this in many hospitals, although some centers still rely on CK-MB.
References
- Wallimann T, et al. (1992). The Biochemical Journal 281 (1): 21–40.
- Wallimann T, et al. (1994). Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 133–135: 193–220.
- Johnsen SH, et al. (2011). Journal of Hypertension 29 (1): 36–42.
- Hekimsoy, Z; Oktem, I. K. (2005). Endocrine research 31 (3): 171–5.
- Johannsen, S; et al. (2013). Muscle & Nerve 47 (5): 677–81.
- O’Dwyer, A. M.; Sheppard, N. P. (1993). Psychological Medicine 23 (2): 323–6.
Be the first to review “Nori Feline CK-MB1 ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.