Nori Equine OSM ELISA Kit
$508.00 – $916.00
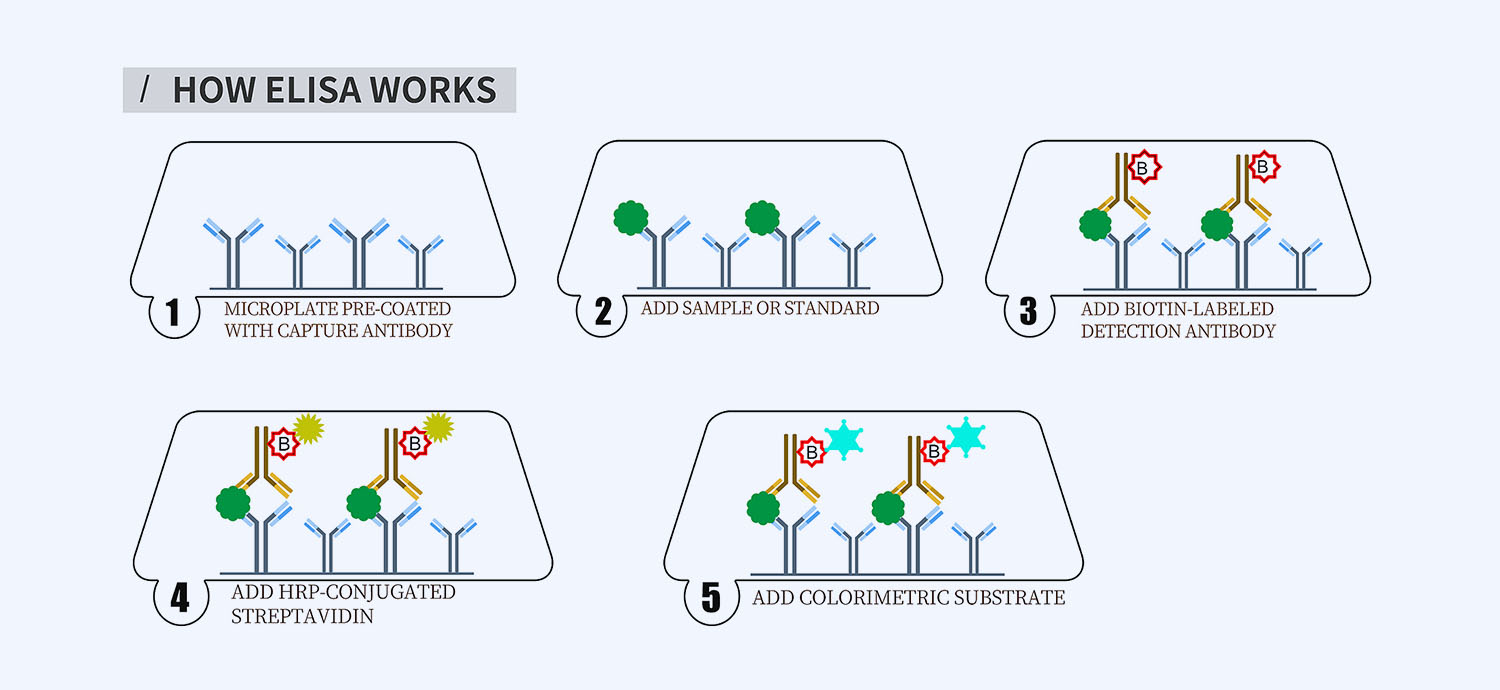
This ELISA kit is for quantification of OSM in horse. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for OSM has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any OSM present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for OSM is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of OSM bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for OSM: Oncostatin M
This product is for laboratory research use only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citation
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Equine OSM ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for OSM: Oncostatin M
Alternative name for equine: Horse
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | na |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
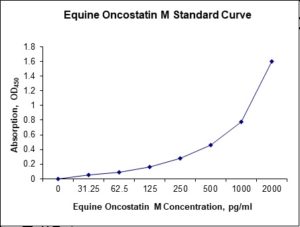
| Sensitivity | 6 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 31.25-2000 pg/mL |
| Specificity | Equine OSM |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Oncostatin M (OSM) is a protein that is encoded by the OSM gene.[1] OSM is a pleiotropic cytokine that belongs to the interleukin 6 group of cytokines.[2] Of these cytokines it most closely resembles leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) in both structure and function.[2] However, it is as yet poorly defined and is proving important in liver development, haematopoeisis, inflammation and possibly CNS development. It is also associated with bone formation and destruction.[3] OSM signals through cell surface receptors that contain the protein gp130. The type I receptor is composed of gp130 and LIFR, the type II receptor is composed of gp130 and OSMR.[4] The role of OSM as an inflammatory mediator was clear as early as 1986.[5] however, its precise effect on the immune system is far from clear although it can serve as both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine. OSM is synthesized by stimulated T-cells and monocytes.[6] The effects of OSM on endothelial cells suggest a pro-inflammatory role for OSM. Endothelial cells possess a large number of OSM receptors.[7] Stimulation of a primary endothelial culture (HUVEC) with hOSM results in delayed but prolonged upregulation of P-selectin,[8] which facilitates leukocyte adhesion and rolling, necessary for their extravasation. OSM also promotes the production of IL-6 from these cells.[7] OSM reduces the degree of joint destruction in an antibody induced model of rheumatoid arthritis.[9] OSM is a major growth factor for Kaposi’s sarcoma “spindle cells”, which are of endothelial origin.[10] These cells do not express LIFR but do express OSMR at high levels.[11] For example, OSM can modulate the expression of IL-6, an important regulator of the host defence system.[7] OSM can regulate the expression of acute phase proteins. OSM regulates the expression of various protease and protease inhibitors, for example Gelatinase and a1-chymotrypsin inhibitor.
References
- Rose TM, Bruce AG (1991). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (19): 8641–5.
- Tanaka M, Miyajima A (2003). Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 149: 39–52.
- Walker EC, et al. (2010). J Clin Invest. 120 (2): 582–92.
- Auguste P, et al. (1997). J. Biol. Chem. 272 (25): 15760–4.
- Zarling JM, et al. (1986). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83 (24): 9739–43.
- Malik N, et al. (1989). Mol. Cell. Biol. 9 (7): 2847–53.
- Brown TJ, et al. (1991). J. Immunol. 147(7): 2175–80.
- Yao L, et al. (1996). J. Exp. Med. 184 (1): 81–92.
- Wallace PM, et al. (1999). J. Immunol. 162 (9): 5547–55.
- Nair BC, et al. (1992). Science. 255 (5050): 1430–2.
- Murakami-Mori K, et al. (1995). J. Clin. Invest. 96 (3): 1319–27.
Be the first to review “Nori Equine OSM ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.