Nori Canine H-FABP ELISA Kit
$508.00 – $916.00
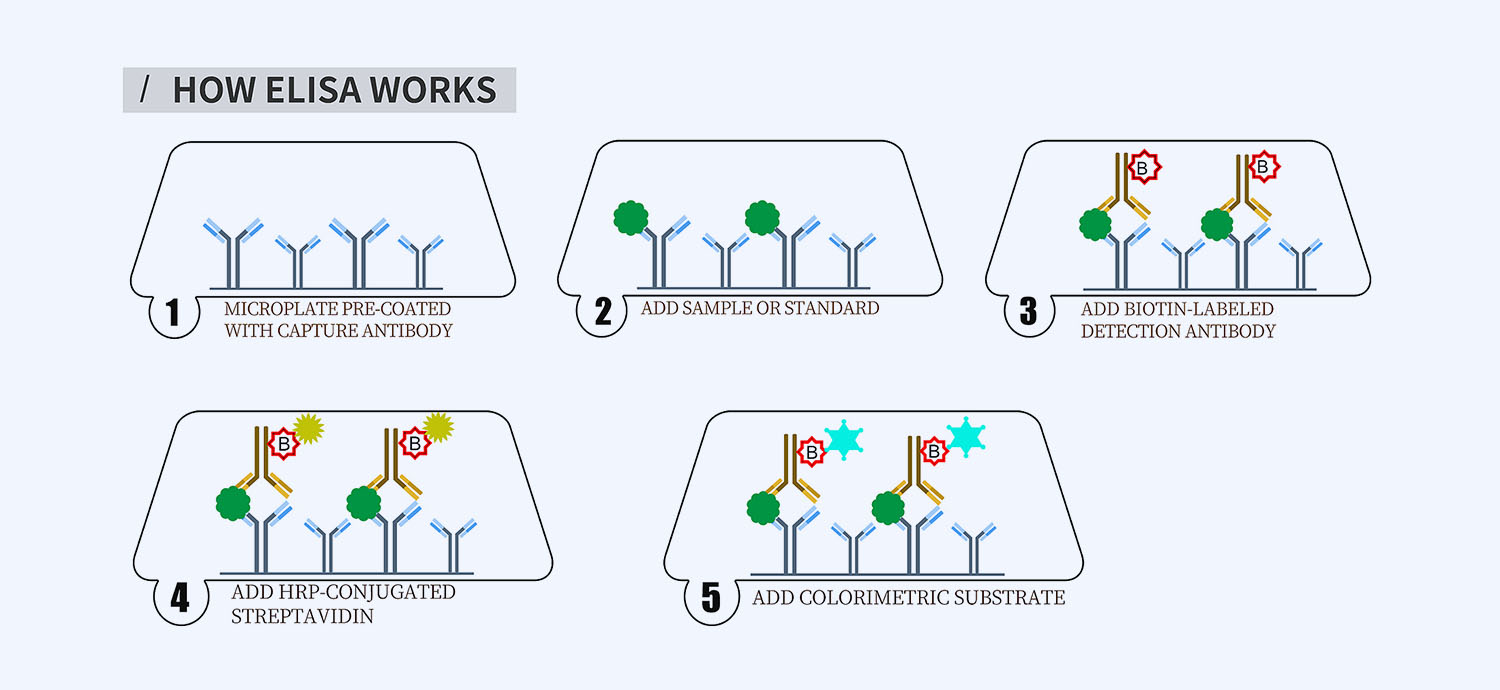
This ELISA kit is for quantification of H-FABP in dog. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for H-FABP has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any H-FABP present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for H-FABP is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of H-FABP bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for H-FABP: Heart-type fatty acid binding protein, FABP3, FABP11, MDG1
This product is for Laboratory Research Use Only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citation (0)
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Canine H-FABP ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for H-FABP: Heart-type fatty acid binding protein, FABP3, FABP11, MDG1
Alternative names for canine: dog
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | A0A8I3MYQ5 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
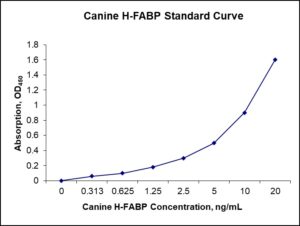
| Sensitivity | 60 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 0.312-20 ng/mL |
| Specificity | Canine H-FABP |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Heart-type fatty acid binding protein (H-FABP) also known as mammary-derived growth inhibitor, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FABP3 gene.[1] Its function is to arrest growth of mammary epithelial cells. It is also a candidate tumor suppressor for human breast cancer. H-FABP is a small cytoplasmic protein (15 kDa) released from cardiac myocytes following an ischemic episode.[2] Like the nine other distinct FABPs, H-FABP is involved in active fatty acid metabolism where it transports fatty acids from the cell membrane to mitochondria for oxidation.[2] H-FABP is a sensitive biomarker for myocardial infarction (MI)[3] and can be detected in the blood within 1-3 hours of the pain. H-FABP is 20 times more specific to cardiac muscle than myoglobin,[4] H-FABP is recommended to be measured with troponin to identify MI and acute coronary syndrome in patients with chest pain. H-FABP measured with troponin shows increased accuracy and sensitivity of 20.6% over troponin at 3-6 hours following chest pain onset.[5] It rapidly release into plasma after myocardial injury – 60 minutes after an ischemic episode,[6] and has tissue specificity. Measuring H-FABP in combination with troponin has a negative predictive value of 98%, could be used to identify those not suffering from MI at the early time point of 3-6 hours post chest pain onset.[5] [6] Alongside D-dimer, NT-proBNP and peak troponin T, H-FABP was the only cardiac biomarker that proved to be a statistically significant predictor of death or MI at one year. Patients who were TnI negative but H-FABP positive had 17% increased risk of all cause mortality within one year compared to those patients who were TnI positive but H-FABP negative.[7] H-FABP has been proven to significantly predict 30 day mortality in acute pulmonary embolism.[8] H-FABP is more effective than Troponin T in risk stratifying Chronic Heart Failure patients.[9]
References
- Phelan CM, et al. (1996). Genomics34(1): 63–8.
- Kleine AH, et al. (1992). Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry116(1-2): 155–62.
- Tanaka T, et al. (1991). Clinical Biochemistry24 (2):
- Ghani F, et al. (2000). Clinical Chemistry46 (5): 718–9.
- Glatz JF, et al. (1994). British Heart Journal71 (2): 135–40.
- Van Nieuwenhoven FA, et al. (1995). Circulation 92 (10): 2848–54.
- Viswanathan K, et al. (2010). Journal of the American College of Cardiology 55: 2590–8.
- Kaczyñska A, et al. (2006). Clinica Chimica Acta; Intl J of Clinical Chem 371 (1-2): 117–23.
- Niizeki T, et al. (2007). Journal of Cardiac Failure 13 (2): 120–7.
Be the first to review “Nori Canine H-FABP ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.
























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.