Nori Canine Endostatin ELISA Kit
$461.00 – $832.00
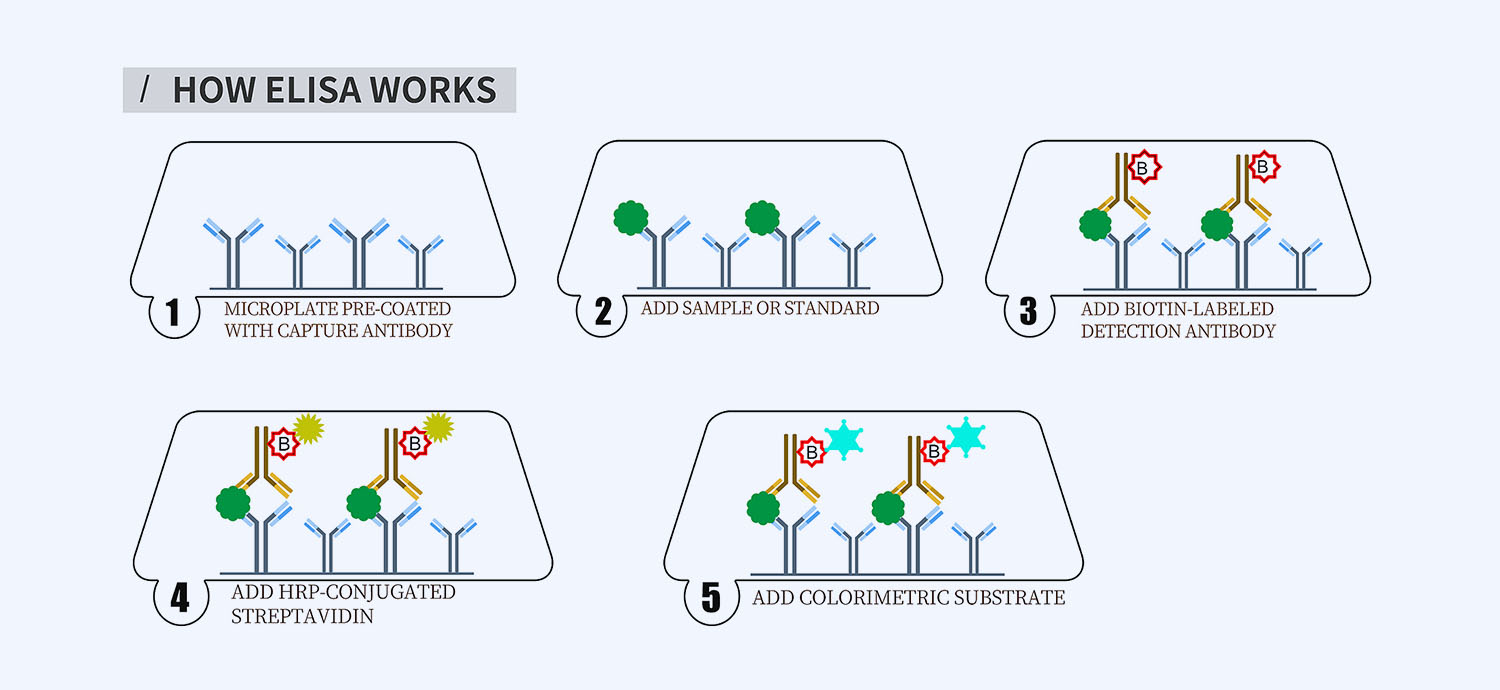
This ELISA kit is for quantification of endostatin in canine. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for endostatin has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any endostatin present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for endostatin is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of endostatin bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for endostatin: COL1A2
This product is for Laboratory Research Use Only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citation (0)
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Canine Endostatin ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for endostatin: COL1A2
Alternative names for canine: dog
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antiben Accession Number | O46392 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
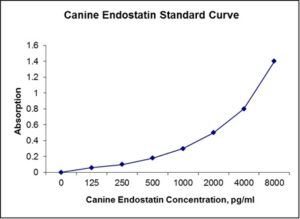
| Sensitivity | 25 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 125-8000 pg/mL |
| Specificity | Canine Endostatin |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Endostatin is a naturally-occurring, 20-kDa C-terminal fragment derived from type XVIII collagen and is a broad-spectrum angiogenesis inhibitor and may interfere with the pro-angiogenic action of growth factors such as bFGF/FGF-2 and VEGF.[1] It was first found secreted in the media of non-metastasizing mouse cells from a hemangioendothelioma cell line in 1997 and was subsequently found in humans.[2][3] It is produced by proteolytic cleavage of collagen XVIII, a member of the multiplexin family that is characterized by interruptions in the triple helix creating multiple domains, by proteases such as cathepsins.[4] Endostatin, as a fragment of collagen 18, demonstrates a role of the ECM in suppression of neoangiogenesis.[2] Overall, endostatin down regulates many signaling cascades like ephrin, TNF-α, and NFκB signaling as well as coagulation and adhesion cascades.[5] In-vitro studies have shown endostatin blocks the proliferation and organization of endothelial cells into new blood vessels.[6] In animal studies endostatin inhibited angiogenesis and growth of both primary tumors and secondary metastasis.[2] Endostatin is currently being studied as part of cancer research. Prior results indicated that endostatin can be beneficial in combinations with other medicines, but endostatin alone gave no significant improvements in tumor/disease progression. Endostatin may also be useful as a therapeutic for inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis as well as Crohn’s disease, diabetic retinopathy, psoriasis, and endometriosis by reducing the infiltration of inflammatory cells through invading angiogenesis.[7] Down’s syndrome patients seem to be protected from diabetic retinopathy due to an additional copy of chromosome 21, and elevated expression of endostatin.[8]
References
- Folkman, J. (2006). Exp. Cell. Res. 312 (5, part 2): 594–607.
- OReilly, M.S.; et al. (1997). Cell 88 (2): 277–85.
- Standker, L; et al. (1997). FEBS Lett 420 (2–3): 129–33.
- Felbor, U; et al. (2000). EMBO J 19 (6): 1187–94.
- Abdollahi, A.; et al. (2004). Mol. Cell 13 (5): 649–63.
- Folkman, J.; Kalluri, R. (2004). “Cancer without disease”. Nature 427 (6977): 787.
- Yin, G., et al. (2002). Mol Ther 5 (5 Pt 1): 547–54.
- Ryeom S, (2009). J Craniofac Surg. 20 Suppl 1: 595–6.
Be the first to review “Nori Canine Endostatin ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.


























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.