Nori Equine Angiopoietin-2 ELISA Kit
$508.00 – $916.00
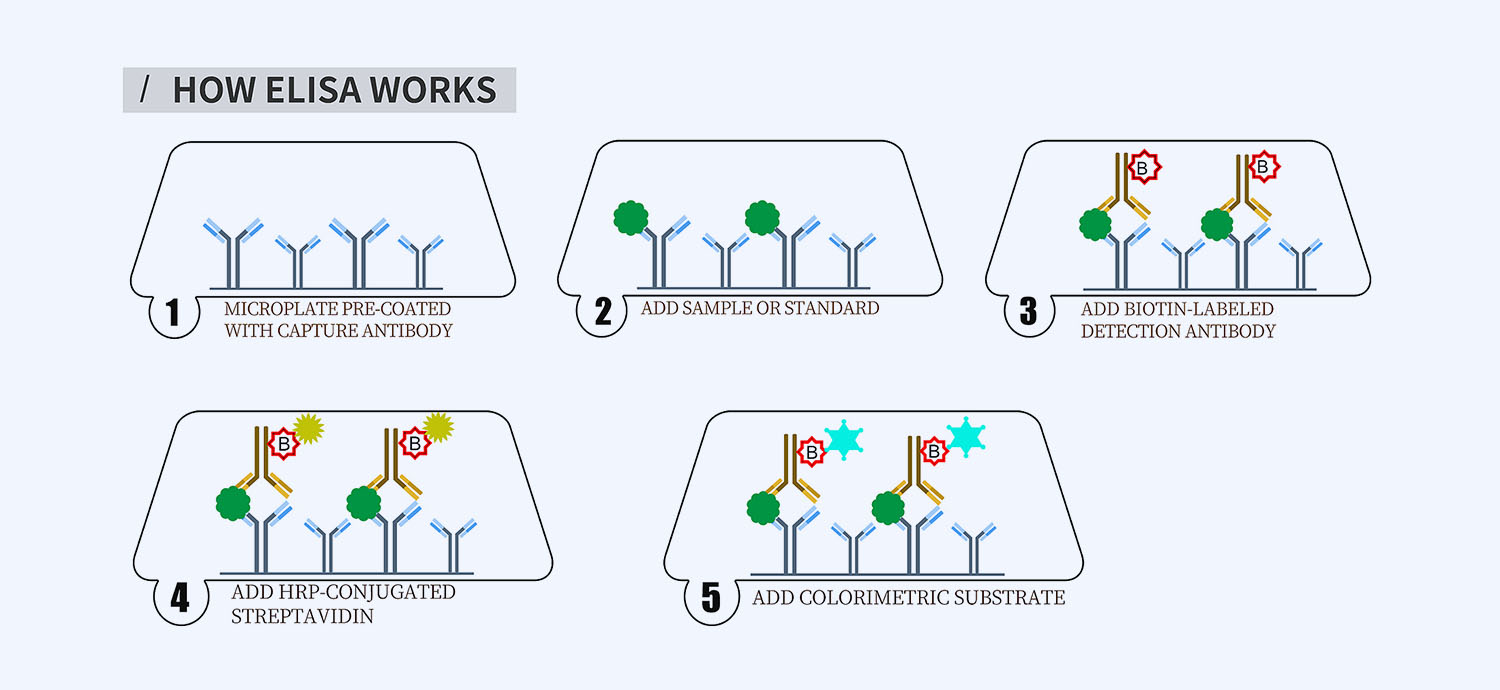
This ELISA kit is for quantification of ANG2 in horse. This is a quick ELISA assay that reduces time to 50% compared to the conventional method, and the entire assay only takes 3 hours. This assay employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique and uses biotin-streptavidin chemistry to improve the performance of the assays. An antibody specific for ANG2 has been pre-coated onto a microplate. Standards and samples are pipetted into the wells and any ANG2 present is bound by the immobilized antibody. After washing away any unbound substances, a detection antibody specific for ANG2 is added to the wells. Following wash to remove any unbound antibody reagent, a detection reagent is added. After intensive wash a substrate solution is added to the wells and color develops in proportion to the amount of ANG2 bound in the initial step. The color development is stopped, and the intensity of the color is measured.
Alternative names for ANG2: Angiopoietin-2,
This product is for laboratory research use only not for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes or any other purposes.
- Description
- How Elisa Works
- Product Citation (0)
- Reviews (0)
Description
Nori Equine Angiopoietin-2 ELISA Kit Summary
Alternative names for ANG2: Angiopoietin-2,
Alternative name for equine: Horse
| Assay Type | Solid Phase Sandwich ELISA |
| Format | 96-well Microplate or 96-Well Strip Microplate |
| Method of Detection | Colorimetric |
| Number of Targets Detected | 1 |
| Target Antigen Accession Number | F6TXD7 |
| Assay Length | 3 hours |
| Quantitative/Semiquantitative | Quantitative |
| Sample Type | Plasma, Serum, Cell Culture, Urine, Cell/Tissue Lysates, Synovial Fluid, BAL, |
| Recommended Sample Dilution (Plasma/Serum) | No dilution for sample <ULOQ; sufficient dilution for samples >ULOQ |
| Sensitivity | 18 pg/mL |
| Detection Range | 93.8-6000 pg/mL |
| Specificity | Equine ANG2 |
| Cross-Reactivity | < 0.5% cross-reactivity observed with available related molecules, < 50% cross-species reactivity observed with species tested. |
| Interference | No significant interference observed with available related molecules |
| Storage/Stability | 4 ºC for up to 6 months |
| Usage | For Laboratory Research Use Only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. |
| Additional Notes | The kit allows for use in multiple experiments. |
Standard Curve
Kit Components
1. Pre-coated 96-well Microplate
2. Biotinylated Detection Antibody
3. Streptavidin-HRP Conjugate
4. Lyophilized Standards
5. TMB One-Step Substrate
6. Stop Solution
7. 20 x PBS
8. Assay Buffer
Other Materials Required but not Provided:
1. Microplate Reader capable of measuring absorption at 450 nm
2. Log-log graph paper or computer and software for ELISA data analysis
3. Precision pipettes (1-1000 µl)
4. Multi-channel pipettes (300 µl)
5. Distilled or deionized water
Protocol Outline
1. Prepare all reagents, samples and standards as instructed in the datasheet.
2. Add 100 µl of Standard or samples to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
3. Add 100 µl of Working Detection Antibody to each well and incubate 1 h at RT.
4. Add 100 µl of Working Streptavidin-HRP to each well and incubate 20 min at RT.
5. Add 100 µl of Substrate to each well and incubate 5-30 min at RT.
6. Add 50 µl of Stop Solution to each well and read at 450 nm immediately.
Background:
Angiopoietin-2 is one of four identified angiopoietins. Angiopoietin-2 promotes cell death and disrupts vascularization. Yet, when it is in conjunction with vascular endothelial growth factors, or VEGF, it can promote neo-vascularization.[1] The expression of Angiopoietin-2 in the absence of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) leads to endothelial cell death and vascular regression. Increased levels of Ang2 promote tumor angiogenesis, metastasis, and inflammation. Effective means to control Ang2 in inflammation and cancer should have clinical value. Ang-2 works with VEGF to mediate angiogenesis. Ang-2 works as an antagonist of Ang-1 and promotes vessel regression if VEGF is not present. Ang-2 works with VEGF to facilitate cell proliferation and migration of endothelial cells.[2] Changes in expression of Ang-1, Ang-2 and VEGF have been reported in the rat brain after cerebral ischemia. [3] Angiopoietin-2 are modulators of endothelial permeability and barrier function. Endothelial cells secrete angiopoietin-2 for autocrine signaling while parenchymal cells of the extravascular tissue secrete angiopoietin-2 onto endothelial cells for paracrine signaling, which then binds to the extracellular matrix and is stored within the endothelial cells. Deregulation of angiopoietin and the tyrosine kinase pathway is common in blood-related diseases such as diabetes, malaria, sepsis, and pulmonary hypertension. This is demonstrated by an increased ratio of angiopoietin-2 and angiopoietin-1 in blood serum. For example, angiopoietin-2 is elevated in patients with angiosarcoma.[4] To be specific, angiopoietin levels provide an indication for sepsis. Angiopoietin-2 is involved in the onset of septic shock. The combination of fever and high levels of angiopoietin-2 are correlated with a greater prospect of the development of septic shock. It has also been shown that imbalances between angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 signaling can act independently of each other. Angiopoietin-2 is produced and stored in Weibel-Palade bodies in endothelial cells and acts as a TEK tyrosine kinase antagonist. As a result, the promotion of endothelial activation, destabilization, and inflammation are promoted. Its role during angiogenesis depends on the presence of VEGF-A.[5] Serum levels of Ang-2 expression are associated with the growth of multiple myeloma,[6] angiogenesis, and overall survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Circulating Ang-2 is a marker for early cardiovascular disease in children on chronic dialysis.[17] Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus induces rapid release of angiopoietin-2 from endothelial cells.
References
- Fagiani E, Christofori G (2013). Cancer Lett 328 (1): 18–26.
- Lim HS, Blann AD, Chong AY, Freestone B, Lip GY (2004). Diabetes Care 27 (12): 2918–24.
- Zan L, et al. (2014). 262: 118–28.
- Amo Y, Masuzawa M, Hamada Y, Katsuoka K (May 2004). J. Dermatol.150 (5): 1028–9.
- Jeansson M, et al. (2011). J Clin Invest 121 (6): 2278–89.
- Pappa CA, et al. (2013). Cancer Invest 31 (6): 385–9.
Be the first to review “Nori Equine Angiopoietin-2 ELISA Kit”
You must be logged in to post a review.



























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.